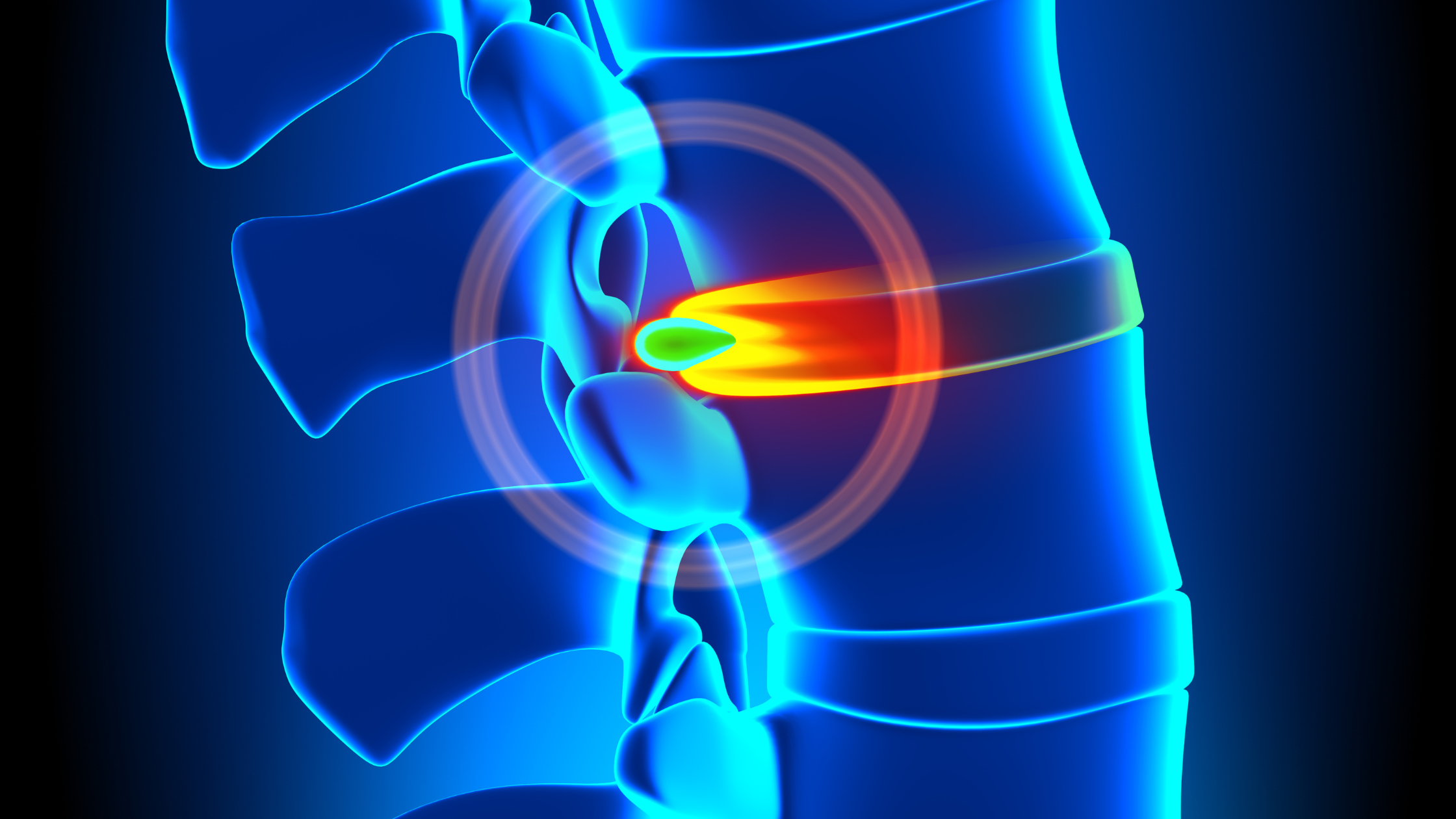
Herniated discs, often referred to as slipped or ruptured discs, are common spinal issues that can cause significant discomfort and mobility challenges. A herniated disc occurs when the soft, gel-like center of a spinal disc pushes through a crack in the tougher exterior casing. This protrusion can irritate nearby nerves, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness in an arm or leg.
The human spine consists of a series of bones called vertebrae, which are cushioned by discs. These discs act as shock absorbers and provide flexibility to the spine. When one of these discs herniates, it can disrupt the normal function of the spine and lead to various symptoms. Understanding the mechanics of the spine and the role of discs is crucial for grasping the implications of a herniated disc.
Herniated discs can occur in any part of the spine, but they are most common in the lower back (lumbar spine) and neck (cervical spine). The severity of the condition can vary, with some individuals experiencing mild discomfort while others may endure chronic pain requiring medical intervention. Recognizing the condition early and seeking appropriate care is essential for effective management.
Key Symptoms of Herniated Discs
Identifying the symptoms of a herniated disc is critical for early diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Pain: It may manifest in the back, neck, arms, or legs, depending on the location of the herniated disc. Lumbar herniated discs often cause pain in the lower back and down the leg (sciatica), while cervical herniated discs can lead to pain in the neck and arms.
- Numbness or Tingling: A herniated disc can cause a loss of sensation or a tingling feeling in the affected area. This occurs when the protruding disc presses against nearby nerves.
- Weakness: Individuals may experience muscle weakness in the affected area, impacting their ability to hold or lift objects.
These symptoms can vary in intensity, and not everyone with a herniated disc will experience severe pain. Some individuals may have a herniated disc without any noticeable symptoms. It is vital to consult a healthcare professional if any of these symptoms persist, as they can also indicate other medical conditions.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of herniated discs. Understanding these can aid in prevention and management. Common causes include:
- Aging: As people age, their spinal discs naturally degenerate and lose moisture content, making them more susceptible to herniation.
- Injury: Trauma or sudden strain, such as lifting heavy objects incorrectly, can cause a disc to herniate.
- Genetics: A family history of disc problems can increase the likelihood of herniation.
Risk factors that heighten the likelihood of developing herniated discs include:
- Occupational Hazards: Jobs that involve repetitive lifting, pulling, pushing, or twisting can increase the risk.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of exercise can lead to weak muscles that support the spine, increasing vulnerability.
- Obesity: Excess body weight adds stress to the discs in the lower back.
Recognizing these causes and risk factors can help individuals take proactive measures to protect their spinal health and reduce the likelihood of developing herniated discs.
Diagnosing Herniated Discs
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment of herniated discs. The diagnostic process typically involves:
- Physical Examination: A doctor will assess the patient’s symptoms and conduct a physical exam to determine nerve function and muscle strength. They may also ask the patient to perform certain movements to identify the source of pain.
- Imaging Tests: If a herniated disc is suspected, imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), or CT (Computed Tomography) scans may be ordered. These tests provide detailed images of the spine, allowing doctors to confirm a herniation and determine its location and severity.
- Nerve Tests: In some cases, nerve conduction studies or electromyography (EMG) may be conducted to assess the electrical activity of nerves and muscles, helping to pinpoint nerve compression.
Early and accurate diagnosis is essential for tailoring treatment plans to individual needs, reducing pain, and preventing further complications. Patients should seek medical advice promptly if they suspect a herniated disc.
Interventional Treatment Options for Herniated Discs
When it comes to treating herniated discs, various interventional options are available, ranging from conservative to more invasive methods. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the symptoms and the patient’s overall health.
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in specific exercises can help strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, improve flexibility, and reduce pain. A physical therapist can tailor a program to address individual needs.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage pain. In some cases, doctors may prescribe stronger medications like muscle relaxants or narcotics for short-term relief.
- Epidural Steroid Injections: These injections deliver corticosteroids directly into the area around the herniated disc, reducing inflammation and alleviating pain.
When Surgery is Necessary
While many individuals find relief from non-surgical treatments, surgery may be necessary in some cases. Indications for surgical intervention include:
- Severe Pain: When pain is persistent and debilitating, and other treatments have failed, surgery may be considered.
- Nerve Damage: If a herniated disc is causing significant nerve compression leading to muscle weakness or loss of bowel or bladder control, surgery may be required to prevent permanent damage.
- Recurrent Herniation: Some patients may experience repeated herniation despite conservative treatment, necessitating surgical correction.
Surgical Options
- Discectomy: The most common surgical procedure for herniated discs, involving the removal of the protruding portion of the disc to alleviate nerve pressure.
- Laminectomy: In some cases, removing part of the vertebra (lamina) may be necessary to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
- Spinal Fusion: This procedure involves fusing two or more vertebrae to provide stability to the spine, often performed in conjunction with a discectomy or laminectomy.
Surgical intervention can offer significant relief, but it is typically reserved for cases where non-surgical treatments have been exhausted.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Herniated Discs
Implementing lifestyle changes can play a crucial role in preventing herniated discs and promoting overall spinal health. Key strategies include:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in activities that strengthen the core muscles, such as swimming, walking, or yoga, can support the spine and reduce the risk of disc herniation.
- Proper Lifting Techniques: Using correct body mechanics when lifting heavy objects can prevent undue strain on the spine. This includes bending at the knees and keeping the back straight.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on the spine, particularly in the lower back.
Additionally, avoiding prolonged periods of sitting, ensuring ergonomic workspaces, and quitting smoking can further contribute to spinal health. By incorporating these habits into daily routines, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing herniated discs.
Managing Herniated Discs for a Better Quality of Life
Herniated discs, while potentially debilitating, can be effectively managed with the right approach. Understanding the condition, recognizing symptoms early, and exploring various treatment options can lead to successful management and recovery. Whether through conservative methods or surgical intervention, addressing a herniated disc can significantly improve an individual’s quality of life.
Adopting lifestyle changes not only aids in recovery but also plays a pivotal role in prevention, serving as a proactive measure against future spinal issues. With the right information and support, individuals can navigate the challenges of herniated discs and enjoy an active, pain-free life.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of a herniated disc, don’t wait to seek professional advice. Early intervention can make a significant difference in managing the condition effectively. Consult with a healthcare provider at Spine Team Texas to explore the best treatment options tailored to your needs and embark on a path to recovery. Remember, your spine health is vital to your overall well-being. Take action today for a healthier tomorrow.